Unit 6
Inversions
Step 1
Unit 13
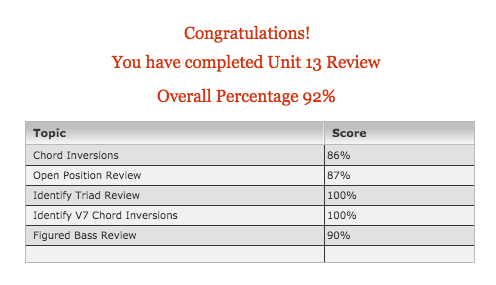
Step 5
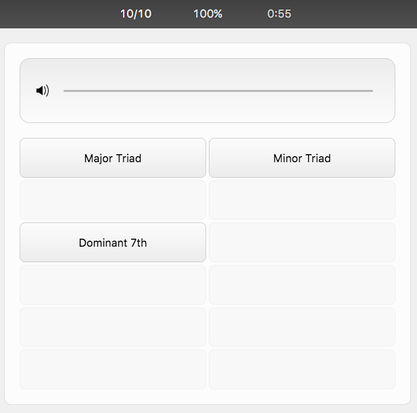
Ear-training
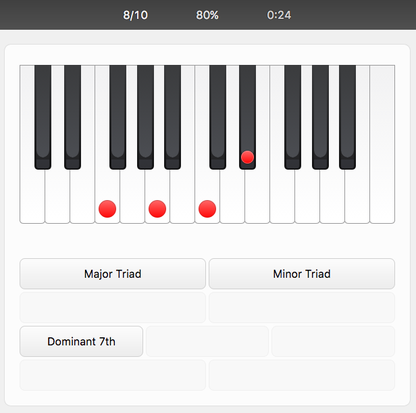
Keyboard
Notes
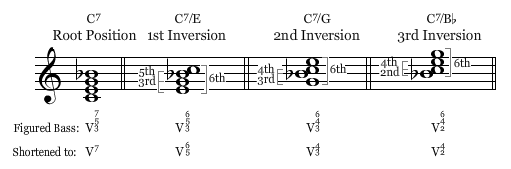
7ths & Inversion Reflection
Step 1
What material would you feel confident explaining to your
classmates?
I believe I would feel confident explaining chord inversions. The concept came to me quite quickly and easily when it was presented.
What material would you not feel confident explaining?
I would not feel confident explaining Figured Bass. I can somewhat understand the concept, but it is still quite confusing to me.
What material do you think you understand but cannot explain at this
point?
The concept I understand but cannot explain would be open and closed position. I understand how they work and how to properly place them, but I have no idea how I
would explain it.
What can you do to prepare yourself to be able to explain this
material?
If I review over the material a bit more and maybe have another person explain it to me, then maybe I will be able to explain the concepts to others.
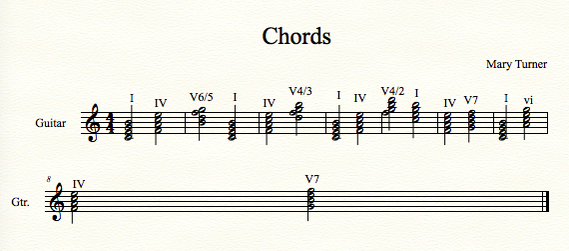
Finale Project/Summative Assessment
Step 1
Create an 8 bar example with half note chords in Finale using traditional & dominant 7th
chords demonstrating a combination of
Root Position
First Inversion
Second Inversion
Third Inversion
Step 2
Label all chords using nomenclature
Secondary Dominant Chords
Step 1
Notes:
Secondary Dominant - chord that has become a major or dominant 7th chord.
Acts as a temporary dominant for another chord.
Can be made from any chord except for I and VII.

Step 2
Secondary dominant chords are chords that are altered from any diatonic chord in a key.
They usually contain an accidental and it has a dominant sound. It usually has a 7th in it, being a minor 7th.
Step 3
Roman numeral nomenclature for each chord:
C - I
G - V
G7 - V7
G9 - V9
C7 - V/IV
F - IV
D7 - V/V
E7 - V/vi
Cadence identification in M14(far, a long, long way to run): Half
Cadence identification at the end of the 1st ending(back to do-oh-oh-oh): Perfect
Cadence identification at the conclusion of the song(do-sol-do): Perfect
2 Secondary Dominant Chords and their resolution:
1. C7 - V/IV
2. D7 - V/V
3. E7 - V/vi
Modulation
Step 1
Notes:
Modulation - changing from one key to another
Adds variety and interest to a piece
Direct - no preparation
Parallel - doesn't change root
Pivot Chord - shared chord for both keys
Most common uses closely related keys (find in the circle of fifths)
Step 2
What is modulation?
The changing from one key to another, usually accompanied by a key signature change.
Why would modulation be used in a composition?
Modulation is used to add variation and keep the interest of the audience. Having the same thing over and over again without any changes would be boring, so adding key changes holds the interest
and adds variety.
What types of modulations are there?
Direct Modulation, where it changes with no preparation; Parallel Chord Modulation, where you change without changing the root; and Pivot Chord Modulation, using a chord to change that both keys
share.
What listening clues heard in the Rainbow Connection indicate a modulation?
Crescendo and partially slowing down, longer notes.
Cite the time of the change and provide the lyric location
2:00
All of us under its spell, We know that it's probably magic
 Getting Started
Getting Started